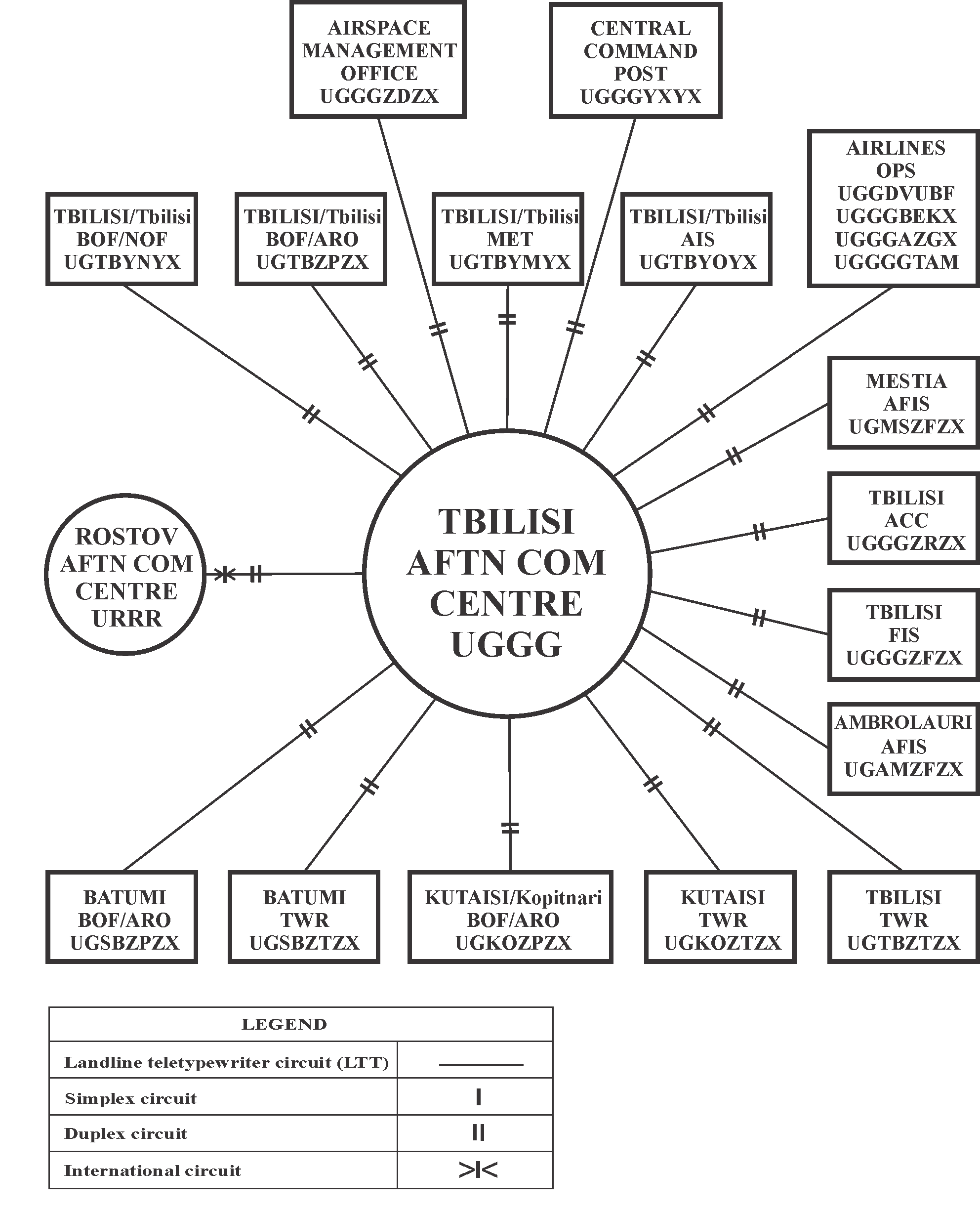
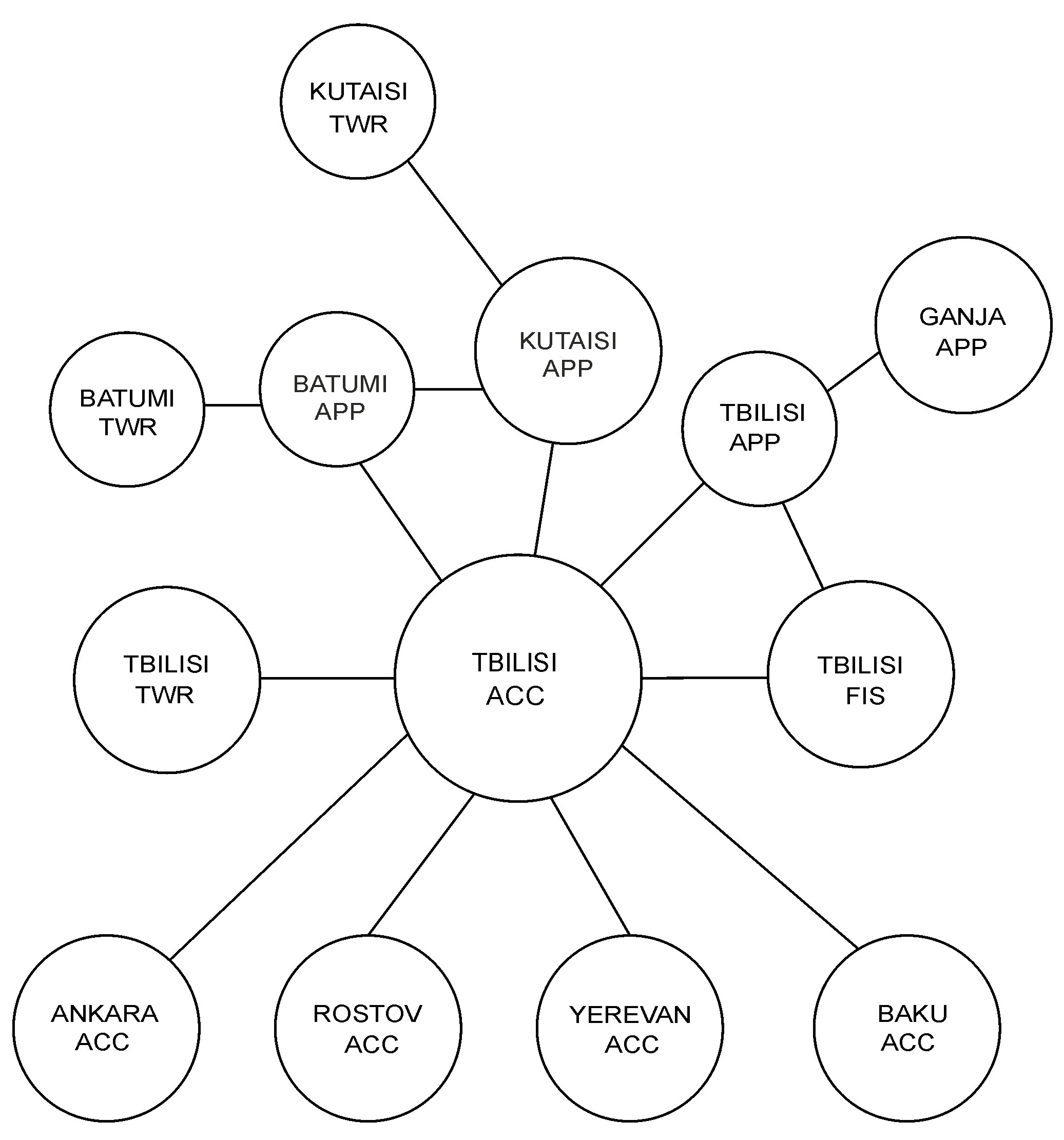
GEN 3.4 Communication and navigation services
1 Responsible service
The responsible authority for the provision of telecommunication and radio navigation services is Sakaeronavigatsia Ltd.
Post: Sakaeronavigatsia Ltd. Tel: (+995 32) 274 42 35 Fax: (+995 32) 274 42 35 AFS: UGGGYTXX |
- Annex 10 — Aeronautical Telecommunications.
- Doc 8400 — Procedures for Air Navigation Services — ICAO Abbreviations and Codes (PANS-ABC).
- Doc 8585 — Designators for Aircraft Operating Agencies, Aeronautical Authorities and Services.
- Doc 7030 — Regional Supplementary Procedures.
- Doc 7910 — Location Indicators.
2 Area of responsibility
Communication services are provided for the entire TBILISI FIR.
Inquiries, suggestions or complaints regarding any telecommunication and radio navigation service should be addressed to Sakaeronavigatsia Ltd and to the authority of the airport of landing.
3 Types of service
3.1 Radio navigation services
- (NDB) Non-Directional Beacon (which are not included in landing systems);
- (DVOR) Doppler VHF Omni-directional radio range;
- (DME) Distance-Measuring Equipment;
- (ILS) Instrument Landing System;
- (OMLOM)
LocatorOuter Marker;(Outer Marker combined withNDBwhich are included in landing systems); - (MM) Middle Marker.
In Georgia, there are no stations associated with special navigation systems such as LORAN, DECCA etc.
3.2 Mobile/fixed service
3.2.1 Mobile service
The aeronautical stations maintain a continuous watch on their stated frequencies during the published hours of service.
An aircraft should communicate with the airground radio station that exercises control in the area in which it is flying. Aircraft should maintain a continuous watch on the appropriate frequency of the control station and should not abandon this watch, except in an emergency, without informing the control radio station.
3.2.2 Fixed service
- They satisfy the requirements of ICAO Annex 10, Vol. II, Chapter 3, par.3.3;
- They are prepared in the form specified in ICAO Annex 10; and
- The text of an individual message does not exceed 200 groups.
3.3 Broadcasting service
Meteorological broadcasts are available on HF and VHF for the use of aircraft in flight. Full details are given in subsection GEN 3.5.
3.4 Language used:
English is used in radiotelephony communications between aircraft and Air Traffic Control units.
3.5 Where detailed information can be obtained
Details of the various facilities available for the en-route traffic can be found in the En-route Part 2 (ENR 4).
Details of the facilities available at the individual aerodromes are to be found in the relevant aerodrome (AD) section. In cases where a facility is serving both the en-route traffic and the aerodromes, details are given in both the en-route part and the appropriate aerodrome section.
4 Requirements and conditions
For reporting points not marked with radio aids the 5-letter name-codes are transmitted.